Inflammation is a double-edged sword. While it is an essential part of your immune system’s defense mechanism, chronic inflammation can wreak havoc on your body, including your eyes. Eye health is often overlooked until it becomes a problem, but understanding the impact of inflammation on vision is critical to protecting and maintaining one of your most vital senses.
The Link Between Inflammation and Vision
Inflammation is your body’s response to injury, infection, or irritants. It’s meant to protect and heal, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to tissue damage, dysfunction, and degenerative diseases. The eyes, being incredibly delicate and highly vascularized organs, are particularly vulnerable. Persistent inflammation in or around the eyes can contribute to conditions that threaten your sight.
The most common pathways through which inflammation affects vision include oxidative stress, immune system dysregulation, and vascular damage. This trio not only accelerates the aging process but also heightens your risk of developing several eye-related diseases.
Eye Conditions Fueled by Inflammation
Chronic inflammation doesn’t just cause discomfort—it can be the underlying driver of some of the most serious eye diseases.
Dry Eye Syndrome is one of the most common manifestations of ocular inflammation. It occurs when inflammation affects tear production or the meibomian glands, leading to redness, irritation, and blurred vision. Left untreated, dry eyes can cause damage to the cornea.
Uveitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. It can cause pain, redness, light sensitivity, and vision loss if not promptly managed. Uveitis is often linked to systemic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or sarcoidosis.
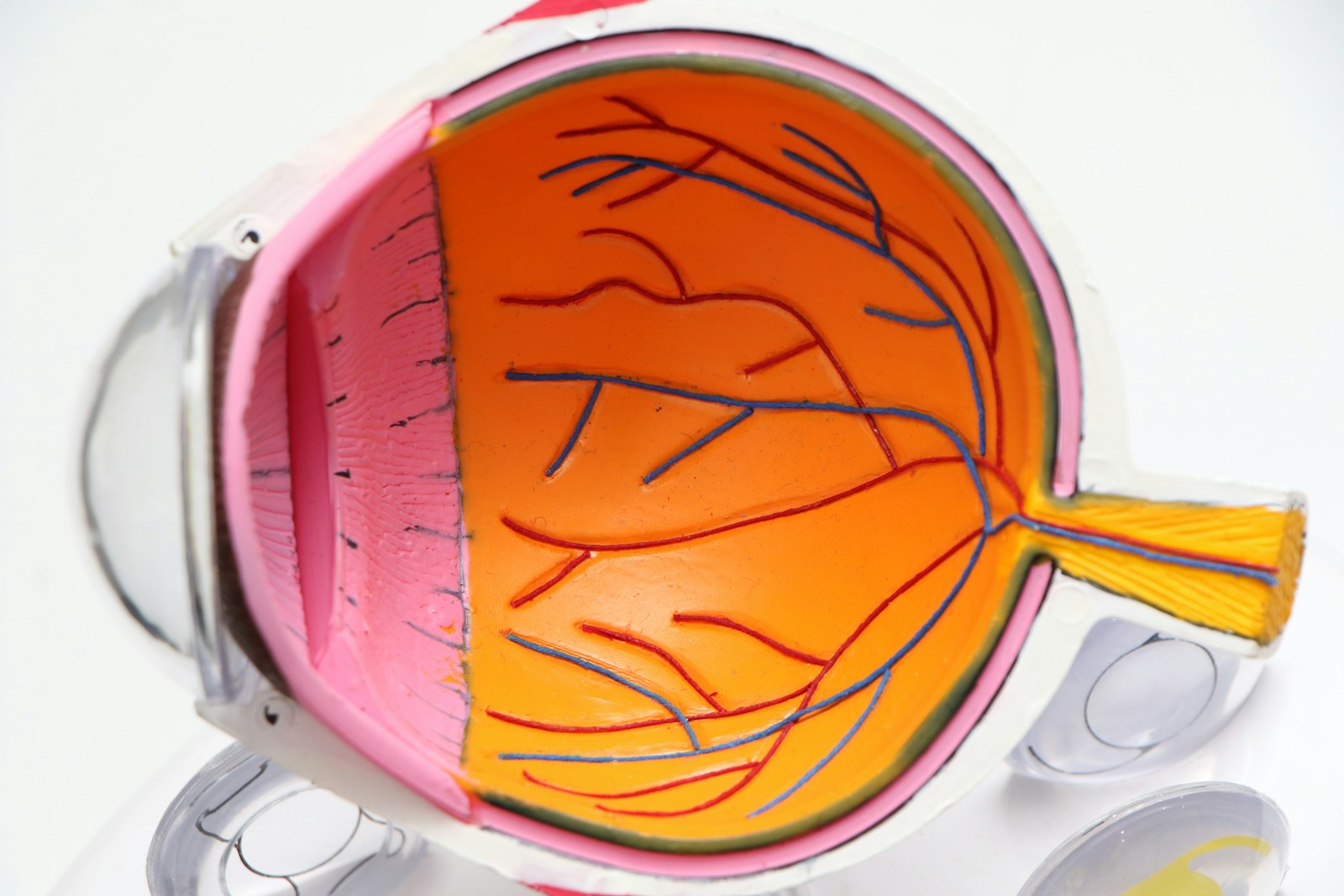
Macular Degeneration, particularly its more aggressive “wet” form, has a strong correlation with inflammation. Chronic low-grade inflammation can contribute to the formation of abnormal blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision impairment and blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes, is exacerbated by chronic inflammation and oxidative stress. Inflammation damages the delicate blood vessels in the retina, leading to swelling, leakage, and tissue damage.
Glaucoma, often referred to as the “silent thief of sight,” is increasingly understood to have an inflammatory component. Elevated intraocular pressure triggers an inflammatory response, causing damage to the optic nerve.
Cataracts, while traditionally associated with aging, have also been linked to chronic inflammation. Prolonged oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators can accelerate the clouding of the lens.
The Development of Inflammation in Vision
Inflammation in the eyes can be triggered by systemic factors or local irritants. Poor diet, high in sugar and processed foods, can promote systemic inflammation that affects eye health. Autoimmune diseases, infections, or exposure to environmental pollutants like smoke or UV radiation can also spark localized inflammation.
At the molecular level, chronic inflammation often involves the overactivation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). These molecules can damage the cells in the retina and disrupt the delicate balance needed for optimal eye function.
Lifestyle Factors That Fuel Inflammation and Impact Vision
Modern lifestyles are rife with habits that fuel inflammation. Poor nutrition, high stress levels, lack of sleep, and excessive screen time all contribute to systemic inflammation, which invariably impacts the eyes. Diets low in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, combined with high consumption of refined carbohydrates and trans fats, create a perfect storm for oxidative stress and inflammation.
Additionally, smoking is a significant risk factor. Tobacco contains toxins that directly damage the blood vessels and tissues in the eyes, amplifying inflammatory pathways.
Prevention and Intervention for Protecting Vision
The good news is that inflammation can be managed and, in some cases, reversed. A proactive approach to reducing inflammation is the key to safeguarding your vision.
Nutrition plays a pivotal role. A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and anti-inflammatory foods can protect against inflammation. Foods like salmon, spinach, berries, walnuts, and turmeric provide the nutrients your eyes need to stay healthy.
Exercise helps regulate the immune system and improve blood flow to the eyes, reducing the risk of inflammatory damage. Even moderate physical activity has been shown to lower systemic inflammation markers.
Stress management is another essential component. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that, when overproduced, can exacerbate inflammation. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can help keep stress in check.
Eye protection is critical in reducing exposure to environmental triggers. Wearing sunglasses that block UV rays and minimizing screen time can protect your eyes from unnecessary strain and inflammation.
Regular eye exams are non-negotiable. They allow for early detection of inflammation-related conditions, enabling timely intervention.
Vision Is Power: Take Control
Inflammation is a silent saboteur, capable of gradually stealing your vision without warning. Protecting your eyes demands a multi-faceted approach, combining lifestyle changes, regular check-ups, and medical intervention where necessary. By understanding and mitigating the impact of inflammation, you can safeguard not just your vision but your quality of life.
